
The ability to solve the puzzles was inconsequential in the study.

Subjects in Group B also underwent the same three rounds of puzzles but received a reward only in round two. Subjects in Group A underwent three rounds of puzzles and never received a reward. In 1971, Deci conducted a study where two groups of people solved simple puzzles. How do we motivate a master, one who has already invested thousands of hours to become a master, to engage in continuous life-long learning? To begin to attack this question, we need to go back a decade before the Dreyfus brothers proposed their model. However, here, we face an educational dilemma. Ongoing education becomes necessary to maintain master status. A disruptive technology or process could even revert a master back to a novice. In fields such as medicine and nursing, where new knowledge, ideas, and methods are constantly being introduced, a master will not stay a master for long. The skill acquisition model was developed with the assumption that students were learning skills in a relatively static domain once a master, always a master. We could deconstruct the training pathway from novice to expert in the medical and nursing educational systems, but there is an equally important consideration. In this light, the role of education is to move a learner from novice to master by exposure to increasingly more real-world and varied contexts. A master may, in fact, not be able to state the rules or the heuristics that they are using. The master is one who makes decisions and takes actions intuitively, even in new contexts.
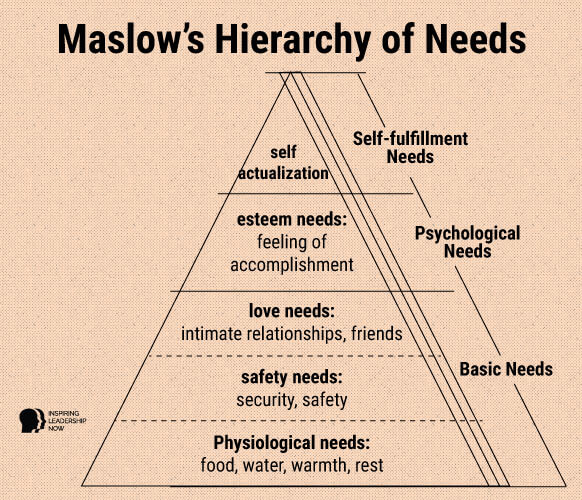
Intermediate stages contain a mix of rule following, combined with more and more sophisticated consideration of context. A novice will simply follow the rules that they are given and not consider context. The phases are characterized by how rules interplay with real-world context. Both theories are founded on the principle that learners pass through five stages: Novice, competence, proficiency, expertise, and mastery. Benner, for example, adapted the skill acquisition model into what is known as From Novice to Expert nursing theory. Others have adapted this model to fit into disciplines other than those of the Dreyfus brothers. The Dreyfus model of skill acquisition was developed around 1980 by the brothers, Dreyfus and Dreyfus. In such a dynamic environment, life-long learning, professional development, and continuing professional education are not just a good idea, they are a necessity. Safe and quality patient care depend on the skills and competence of the professional caring for them.

The technologically advanced and super-charged pace of today's society poses a multitude of challenges in the medical and nursing professions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
